Risk assessment is one of the major components of a risk analysis. Risk analysis is a process with multiple steps that intends to identify and analyze all of the potential risks and issues that are detrimental to the business. This is an ongoing process that gets updated when necessary. These concepts are interconnected and can be used individually.
To ensure the success of your project, effective risk management is vital at every phase. We offer a comprehensive range of risk management and assessment services that can help you take a structured approach to managing risk at every stage of your project.
Beyond complying with legislative requirements, the purpose of risk assessments is to eliminate operational risks and improve the overall safety of the workplace. It is employer’s responsibility to perform risk assessments when:
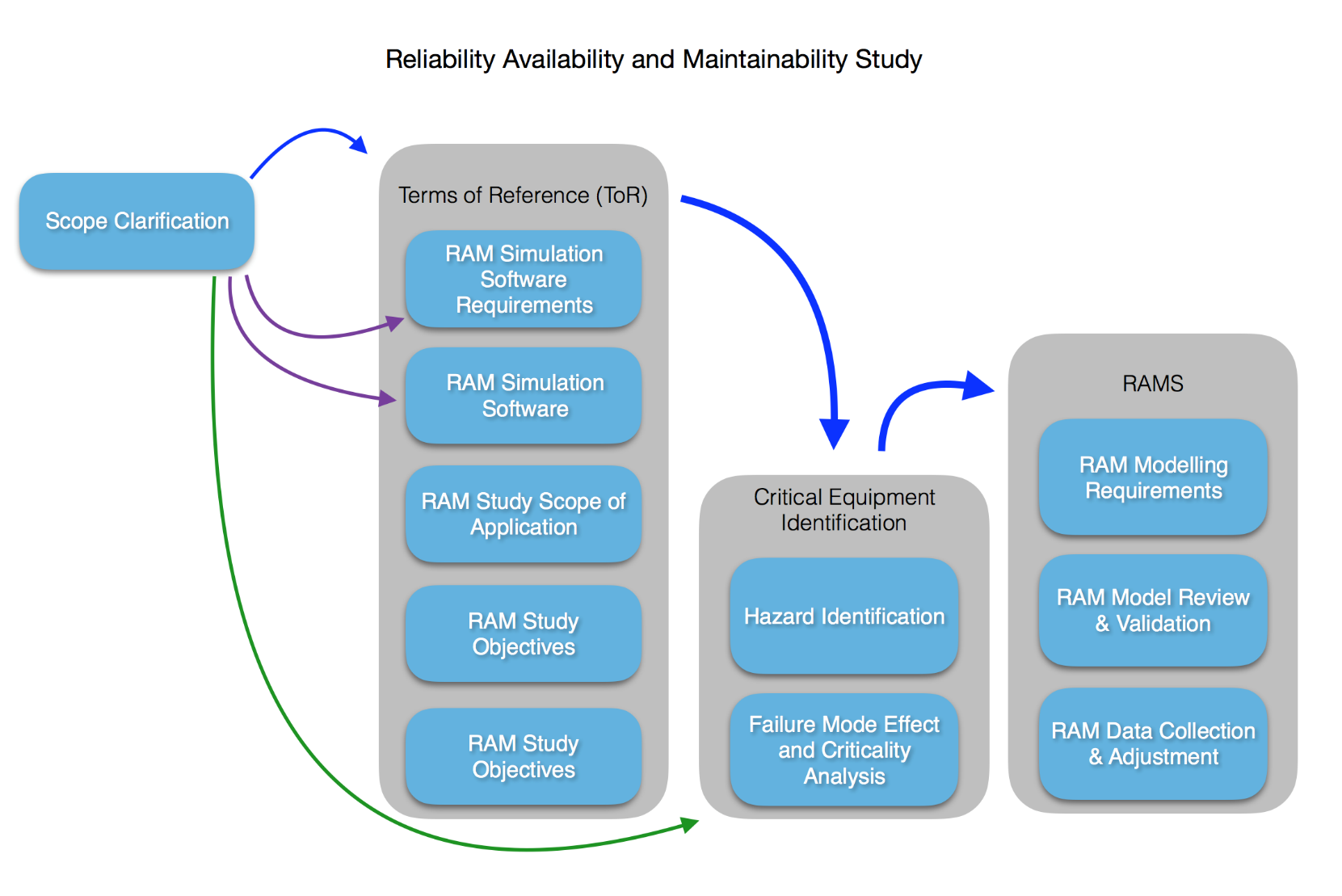
Objectives of a RAM Analysis
Our expert team of consultants have been proving Reliability, Availability and Maintenance studies and analysis for various industries. The main objectives of a RAM analysis, is for it to be used as a decision-making tool to increase the availability of the system, and thus increase the overall profit as well as reducing the life cycle costs (inclusive of the cost of maintenance, lost production, operating etc). RAM analysis can be carried out on systems and facilities of different types and sizes in various industries ranging from oil and gas, water and waste water treatment, nuclear, process, manufacturing and many more.
One of the best ways to make a production or process plant more productive and profitable is to make it more reliable. This can be done by lowering the amount of unexpected downtime and the amount of time needed for regular repairs and changeovers. The first step in achieving these goals is to use Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability (RAM) models to look at the engineering and planning of the building.
What is a Risk Register?
A Risk Register is an archive of: documented risks, their risk levels, and current/planned actions to mitigate the risks. Organizations use this document for general risk management. Using it for identifying, tracking and mitigating/treating risks. It is also useful to have such a document for regulatory compliance purposes. It can also serve as evidence for continual improvement.
Typically, risks are assigned to a risk owner. This will also be recorded in the register. A risk owner is an individual who is ultimately accountable for the risk (ensuring that it is managed properly).
The first step is to produce an asset register – i.e. a list of hardware, software, devices and databases on which sensitive information is stored. After all, it’s only once you know what needs to be protected that you can determine the threats associated with them and put in place appropriate defenses. An information asset is any piece of information that is of value to the organization.
An asset-based risk assessment begins with an asset register. This document specifies all the places where you keep sensitive information. The newly acquired equipment's specifications and Equipment number, along with the corresponding piping circuits (RBI). Enter all data into the master data plan and update it in software.
Once the asset register has been produced, the next step is to create an asset risk register to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that could pose risks to those assets. A vulnerability is a weakness that can be exploited by one or more threats. Once threats and vulnerabilities have been identified, the risks should be analyzed to establish the damage that they can cause. This needs to consider how the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data can be affected by each risk.
Asset Criticality Assessment (ACA) is a tool that you can use to define the criticality of a system and the individual locations and pieces of equipment that make up that system. The ACA interface lets you define the probability and consequences of the failure events that may occur for a system, which helps you determine which of your systems, locations, and pieces of equipment have the highest risk of failure in your facility y. In other words, using an ACA, you can determine which of your systems, locations, and pieces of equipment are critical.
A CA (Criticality Assessment) system is a collection of equipment organized into systems to facilitate APM study. For the work process of criticality assessment, systems are primarily classified into three categories. Process / Non-Process Systems / Piping Systems.
Asset performance management approaches for new projects or during the operational and maintenance stages of industrial facilities and plants are based on CA. Based on how significant an asset or system is to the operating unit, its staff, and its stakeholders, a priority is established. Criticality assessment is a risk-based method for ranking the assets and systems according to the likelihood and effects of various scenarios that could occur over their lifecycle. The outcomes are chosen taking into account the risk matrix. Financial, reputational, and EHSS considerations.
Many accidents arise because employees do not understand the hazards involved or the necessary precautions. New risks may be introduced into the workplace through changes in techniques, new plants and equipment, new materials or a change of contractors. It is therefore necessary for management to assess the potential and hidden hazards associated with these changes. This course provides participants with the techniques of risk assessment and assists them in preparing safe systems of work and good safety practices.
The RIS approach is applicable to instruments and devices that are installed in safety instrumented systems (SIS), and it is based on principles that have been derived from international standards for safety instrumented systems (SIS) and functional safety systems (IEC 61508/61511).
The Safety Instrumented Systems (SIS) and important process protective instrumentation proof test strategies are optimized using the RIS approach. The maintenance strategies of SIS are defined using LOPA investigations, SIL evaluation, and SIL validation procedures.
The RIS technique is applicable to all instruments and devices used for equipment protection and Safety applications exclusively. It is based on the ideas that have been taken from international standards for SIS and functional safety systems (IEC 61511), and it was developed using those standards.
Following diagram illustrates high-level workflow of PK RIS methodology:
RCM is a process that ensures an asset continues to accomplish what it is designed to do in the operating context in which it is currently being used. It is used to identify and optimize the preventive maintenance actions that should be completed to limit the related risks of losing the function of the assets. This can be done by comparing the current state of the asset with its previous state. In addition to this, condition monitoring and the determination of essential spare component requirements are also included. RCM refers to a procedure that assures an asset continues to perform the functions for which it was meant to do in the context in which it is now operating. Its purpose is to determine and improve the preventive maintenance procedures that need to be carried out in order to reduce the risks connected with the function of the assets being lost. Client shall apply RCM methodology for systems based on the system criticality assessment (as per Asset Criticality Assessment Procedure OMS-433, for reference) results as following:
The purpose of this standard is to describe the process, approach, and requirements that must be met in order to ensure the effective implementation and continuous practice of Inspection Integrity Management. In the event that a capital project involves the replacement or addition of RBI stationary equipment, an RBI assessment must be carried out during the engineering and design phase in compliance with SABIC Reliability in Design OMS 411.
Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) is a systematic approach to enhance the inspection of stationary or pressure system equipment by establishing inspection intervals that are suitable for age-related degradation mechanisms and implementing monitoring/verification inspections.
Regarding mechanisms of deterioration that are not related to age. The main objective of the RBI (Risk-Based Inspection) methodology is to mitigate the risk of pressure boundary failure caused by material deterioration.
In cases where the use of RBI for inspection policies is prohibited by local legislation, it is still recommended to utilize RBI for enhancing comprehension of equipment degradation and creating targeted written examination schemes. This approach will mitigate the likelihood of unforeseen equipment malfunctions. The methodology utilized for RBI must adhere to the standards set forth in 'API 580/581 Risk Based Inspection'.